Connect With Us
Diabetes and Your Feet
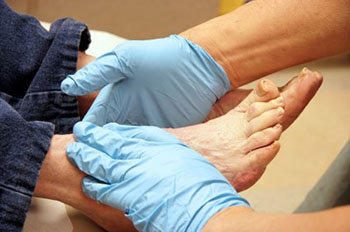
Diabetes, or hyperglycemia, is high blood glucose. Diabetes is a chronic disease that affects over 25 million Americans of all ages; as many as one in three adults in the United States will have high blood sugar levels indicating diabetes.
There are different types of diabetes: type 1 (also called juvenile diabetes because it is usually diagnosed in children and young adults), type 2 (the most common form of diabetes that results from insulin resistance; insulin resistance occurs over time as the body fails to make enough insulin to effectively regulate blood glucose, and gestational (occurs during pregnancy). If blood sugar levels are not normalized in a diabetic, the body may have trouble fending off infections due to decreased functioning of the immune system. This can affect the feet in particular due to peripheral artery disease (lack of circulation) and peripheral neuropathy (loss of feeling).
As a result of diabetes, the feet may become susceptible to a slew of problems, such as ulcers and wounds that do not heal properly, fungal infections, ingrown or brittle toenails, corns, calluses, hammertoes, athlete’s foot, and cracked or dry skin. Gangrene, or dead tissue, can develop, causing bacterial infections that may result in amputation of the affected areas. Even every day activities such as walking can cause issues in the feet of a diabetic, as the bones, joints, and skin are affected by the condition.
For the diabetic, proper and thorough foot care is imperative. Here are proper foot care suggestions for diabetics to follow:
- Check feet daily to detect foot problems, changes, or injuries early on
- Keep feet clean, warm, and dry (thoroughly dry between toes)
- Wear comfortable shoes and do not wear the same pair every day (look for roomy toe boxes, leather uppers, and shoes that do not pinch, rub, or cause pressure; avoid stiff shoes and gradually break-in new footwear)
- Always wear clean, dry socks without tears or irritating seams (thin cotton is absorbent and helps keep feet dry)
- Do not leave feet exposed or unprotected (sleep in loose socks; do not wear flip flops or sandals; do not go barefoot)
- Never expose feet to heat or high water temperatures (burns can occur due to loss of feeling)
- Maintain better foot circulation (do not smoke; avoid stockings or socks with tight elastic bands; do not cross feet or legs when sitting)
- Treat the feet gently (pat dry; avoid cutting or tearing the skin)
- Carefully shape toenails straight across with an emery board (avoid ingrown toenails)
- Do not use over-the-counter foot products such as antiseptic solutions, plasters, tapes, or anything sticky (they can damage the skin and lead to wounds)
- Use moisturizer to keep skin supple (except between toes)
- Do not treat corns or calluses at home; see a doctor for care
It is important that diabetics seek podiatric care on a regular basis to prevent foot problems that can easily get out of control. A podiatrist will ensure proper foot care, from maintenance to the treatment of any developing problems. Any foot problem should be immediately addressed in a diabetic to avoid serious complications.
