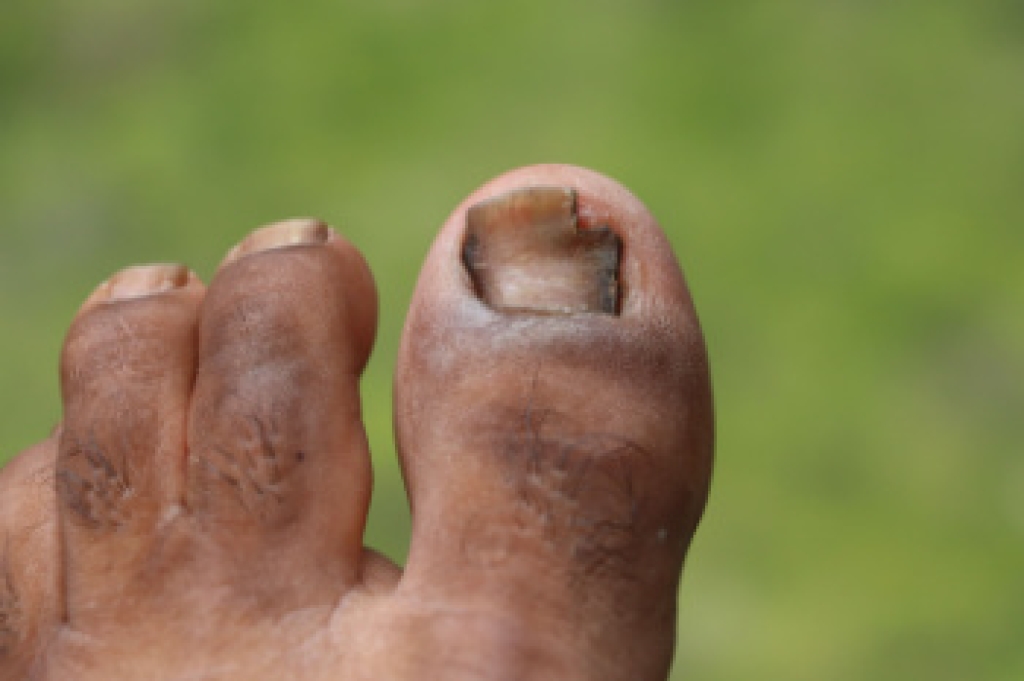
Toenail fungus often begins quietly, showing up as a small change in color or texture before spreading deeper into the nail. Over time, the nail can become thick, brittle, and difficult to trim, and shoes may feel uncomfortable because of pressure on the affected area. Warm, moist environments encourage fungal growth, which is why people who wear closed shoes for long hours or visit communal spaces like gyms and pool areas are more at risk. Although over-the-counter products can be tempting, established fungal infections rarely clear without professional care. A podiatrist can confirm the diagnosis, thin the nail if needed, and recommend targeted treatments that reach the source of the problem more effectively. Addressing the issue early can prevent pain, nail deformity, and spread to other toes. If you notice persistent discoloration, thickening, or crumbling of a toenail, it is suggested that you see a podiatrist for a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
If left untreated, toenail fungus may spread to other toenails, skin, or even fingernails. If you suspect you have toenail fungus it is important to seek treatment right away. For more information about treatment, contact our podiatrists of Superior Foot & Ankle Center. Our doctors can provide the care you need to keep you pain-free and on your feet.
Symptoms
- Warped or oddly shaped nails
- Yellowish nails
- Loose/separated nail
- Buildup of bits and pieces of nail fragments under the nail
- Brittle, broken, thickened nail
Treatment
If self-care strategies and over-the-counter medications does not help your fungus, your podiatrist may give you a prescription drug instead. Even if you find relief from your toenail fungus symptoms, you may experience a repeat infection in the future.
Prevention
In order to prevent getting toenail fungus in the future, you should always make sure to wash your feet with soap and water. After washing, it is important to dry your feet thoroughly especially in between the toes. When trimming your toenails, be sure to trim straight across instead of in a rounded shape. It is crucial not to cover up discolored nails with nail polish because that will prevent your nail from being able to “breathe”.
In some cases, surgical procedure may be needed to remove the toenail fungus. Consult with your podiatrist about the best treatment options for your case of toenail fungus.
If you have any questions please contact our office located in Long Beach, CA . We offer the newest diagnostic and treatment technologies for all your foot and ankle needs.